What is the Green Grid Network(GGN) ?
The Green Grid Network(GGN) is an decentralized energy management system that uses blockchain and decentralised autonomous organisation (DAO) technology to improve the efficiency, reliability, security, and transparency of the electrical grid.
Key Components
Blockchain Platform: A secure, distributed ledger technology forms the backbone of this network. It records all transactions, energy generation data, appliance status, and other key information. Smart contracts embedded in the blockchain automate trades, implement demand-response programs, and manage microgrid coordination.
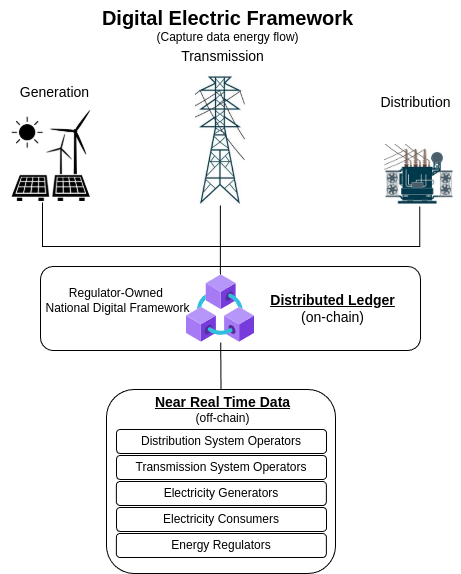
Digital Electric Framework, records data energy flow from all levels of the electricity network, from generation to consumption. And makes it available to authorized players by the Energy Regulator.
Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO): The DAO provides a democratic governance structure. Consumers, prosumers, energy providers, and other stakeholders participate in decision-making regarding grid optimization, resource allocation, and investment.
Microcontrollers: These small, programmable devices are integrated with diverse energy assets:
Renewable Generation: Microcontrollers monitor and control the output of solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage systems.
Flexible Loads: Attached to smart appliances, EV chargers, and heat pumps, microcontrollers enable their energy consumption to be shifted or curtailed based on grid needs.
Microgrid Networks: Microcontrollers manage energy flow, switching between on-grid and off-grid operation for localized resilience.
Key Network Operations
Data Collection: Microcontrollers continuously sense and transmit data about energy production, consumption patterns, and appliance status to the blockchain.
Algorithmic Decision-Making: Smart contracts and DAO governance protocols analyse this real-time data along with market information to optimize energy dispatch and maintain grid stability.
Actionable Instructions: The blockchain network sends instructions to microcontrollers, prompting them to adjust energy generation, curtail or shift energy use of appliances, or initiate microgrid islanding/reconnection procedures.
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Trading: The blockchain facilitates a secure marketplace where individuals or communities can directly trade surplus renewable energy with neighbours or within their microgrid.
Benefits
Enhanced Resilience: The system rapidly responds to disruptions or fluctuations in supply and demand, improving network stability under the pressures of increasing electrification.
Optimized Integration of Renewables: Better management of variable power generation and storage for reliable electricity supply.
Active Demand-Side Management: Microcontrollers provide fine-grained control for maximizing efficiency and flexibility in energy usage.
Empowered Microgrids: Microgrids are fully integrated, contributing to both local and overall grid resilience.
Consumer Empowerment: Participants have a voice through the DAO and can actively manage their energy production and consumption.
Transparency and Traceability: The blockchain provides a transparent and immutable record of all energy-related activities.
This innovative network reimagines the electricity grid as a collaborative, adaptable, and hardware-integrated system. It's a framework that harnesses the power of emerging technologies to build a more secure, reliable, and democratic energy future.